Whether during a dental visit, or conducting your own research about your teeth, you’ll undoubtedly encounter a flurry of unfamiliar terms and jargon used by dental professionals. From discussions about crowns and root canals to mentions of calculus and periodontitis, navigating the sea of dental terminology can be overwhelming. So we’ve created this article for your reference whenever you come across unknown dental terms. We believe with this knowledge, you can better understand your own oral health and actively engage in discussions with your dental care providers.
Dental Terminology:
Abscess
A localized collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection.
Amalgam
A filling material composed of a mixture of metals, such as silver, tin, and mercury. It is used for the dental restoration of teeth that have have been affected by decay or damage.
Bruxism
The act of grinding or clenching one’s teeth, ofen done unconsciously, which can lead to tooth wear and other dental problems.

Calculus
Also known as tartar, it is hardened dental plaque that forms on teeth and can only be removed by a dental professional.
Caries (or cavities)
Commonly referred to as tooth decay or cavities, it is the detrioration of tooth structure caused by bacteria and acid
Crown
There is the anatomical crown which is the portion of tooth that is visible above the gums and is normally covered by, and includes, the enamel. A dental or artificial crown is a restoration that covers or caps a damaged or decayed tooth, restoring its shape, size, strength, and appearance.
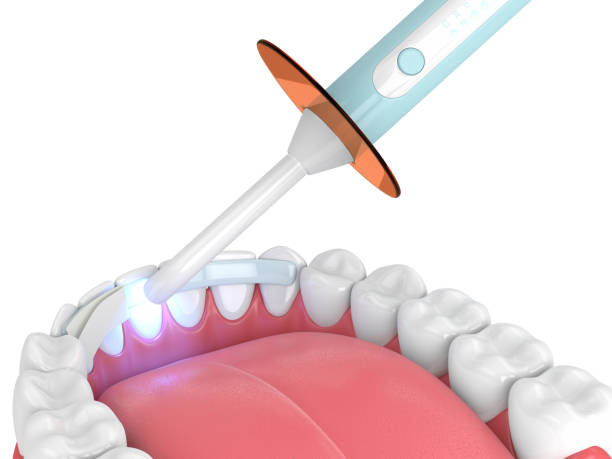
Dental Bonding
A cosmetic dental procedure by which a tooth-coloured resin material applied and hardened with a special light, bonding, it to the tooth. It is commonly used to repair chipped or cracked teeth, improve the appearance of discoloured teeth and ever alter the shape of teeth
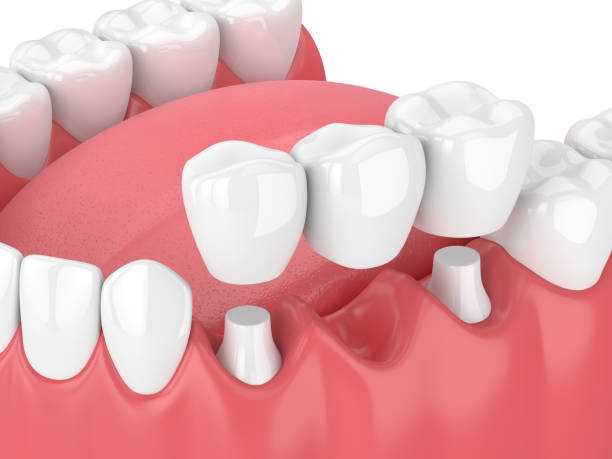
Dental Bridges (also known as fixed partial dentures)
Restorative dental devices used to replace one or more missing teeth. They consist of one or more artificial teeth, known as pontics (that bridge the gap in your teeth) and are anchored on each side by crowns attached to adjacent natural teeth or dental implants.
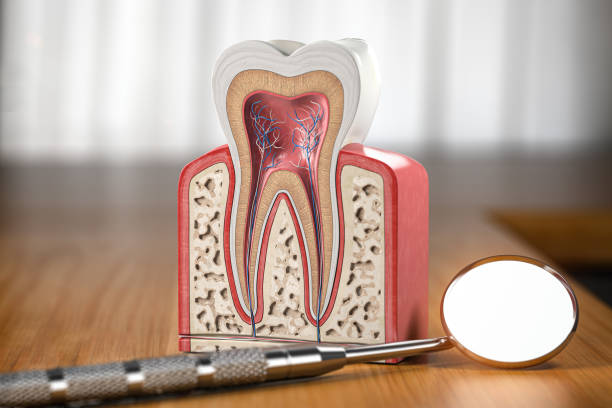
Dentin
The layer of ttoth structure beneath the enamel that forms the main body of the tooth.
Dentures
Removeable prosthetic devices that replace multiple missing teeth or a full arch of teeth. Dentures can be complete (replacing all teeth in an arch) or partial (replacing only some teeth in an arch).
Enamel
The outermose layer of the tooth that serves as a protective covering.
General Anesthesia
A medical state induced in a patient to ensure loss of consciousness. It is typically administered through intravenous (IV) injection or inhalation. Under general anaesthesia, the patient is completely unaware and doesn’t feel any pain or discomfort through the procedure.
Gingiva (Gingival tissue)
The soft tissue surrounding and supporting the teeth; commonly known as the gums.
Gingivitis
A mild form of gum disease characterized by the inflammation of the gum tissues, caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth and gum line. Symptoms include bleeding during brushing or flossing, and slightly swollen, tender gums.
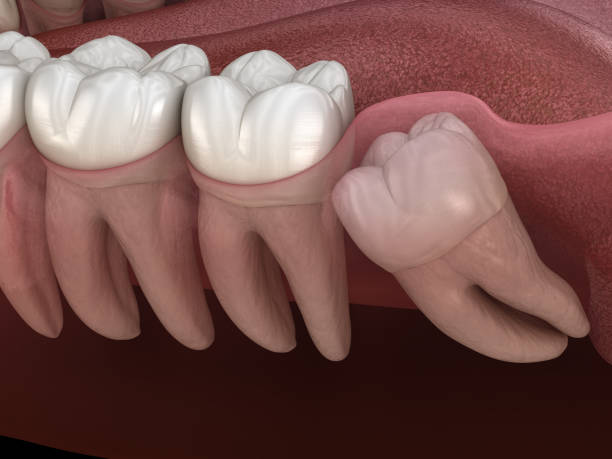
Impacted tooth
A tooth that fails to emerge or fully grow into its normal position within the jawbone. Wisdom teeth are a common example of impacted teeth due to people not having enough space in their mouth for them. Most people will have to undergo a surgical procedure to remove wisdom teeth. However, no treatment may be needed if the impacted tooth is not causing any problems. Your dentist will talk you through the best treatment plan should it be discovered you have an impacted tooth.
Implants
Prosthetic tooth roots that are surgically placed into the jawbone, serving as the foundation for replacement teeth, such as crowns, bridges, or dentures. Dental implants can be surgically placed in the mandibular and/or maxillary bone (the lower and upper jaw bone, respectively).

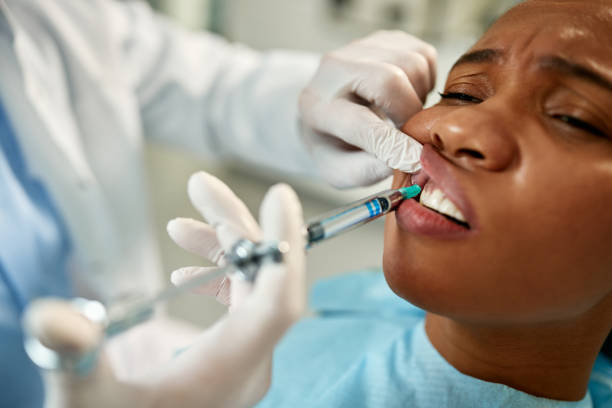
Local Anaesthesia
The administration of an anaesthetic agent, usually through injection, close to the targeted are to block nerve signals, temporaily preventing pain while allowing the patient to remain conscious during the procedure.
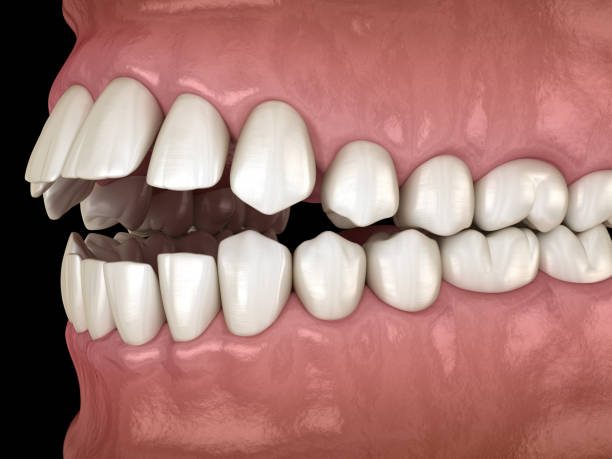
Malocclusion
A misalignment of the teeth and/or jaws, resulting in an improper bite. Orthodontic treatment is typically used to realign the teeth and/or jaws.
Oral Cavity
Known as the inside of the mouth or buccal cavity.
Oral hygiene
The practice of maintaining cleanliness of the mouth and teeth to prevent dental problems, such as tooth decau and gum disease.

Periodontal Disease (or Gum Disease)
An inflammatory condition that affects the gums and supporting structure of the teeth. This is a broad term that encompasses both gingivitis (early stages) and periodontitis (late stages).
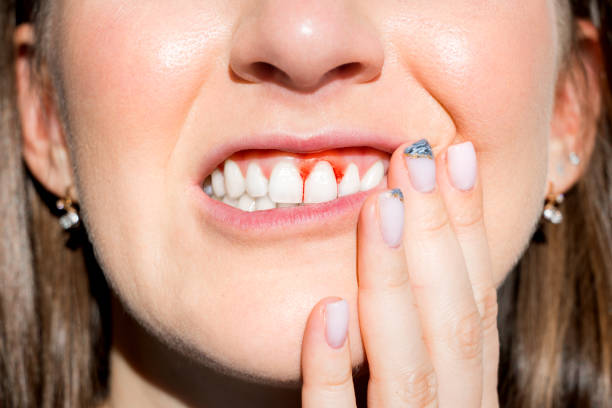

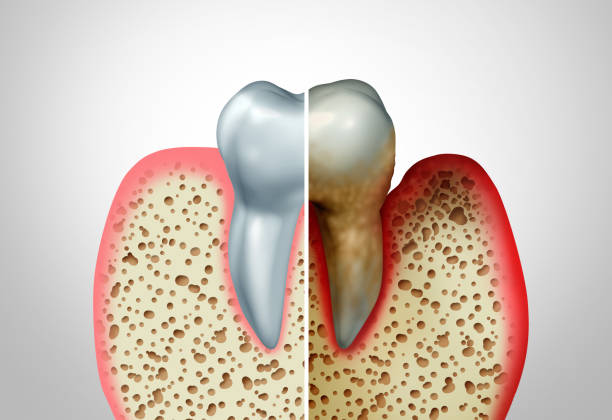
Periodontitis
A serious gum infection that damages the soft connective tissue surrounding the structure of teeth and destroys the bone supporting the teeth, which can lead to tooth and bone loss if left untreated.
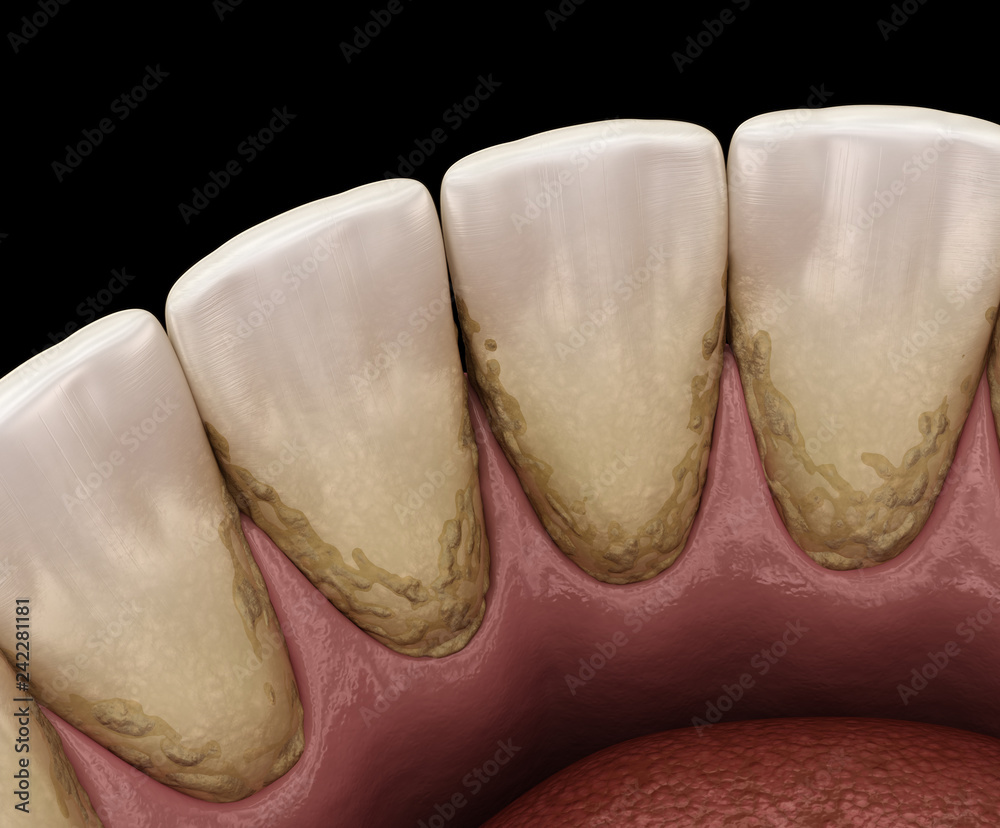
Plaque
A sticky film of bacteia that forms on teeth and can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease if not properly removed.
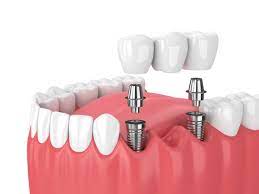
Prosthesis
An artificial dental appliance that’s used to replace missing teeth. A dental prothesis is designed to restore functionality, aestheitics and proper alignment of the teeth and jaw. This includes dentures, dental bridges, dental crowns and dental implants.
Root canal
A dental procedure involving the removal of the infected or damaged pulp (nerve tissue) from the root canal space of a tooth, followed by sealing and filling the space.
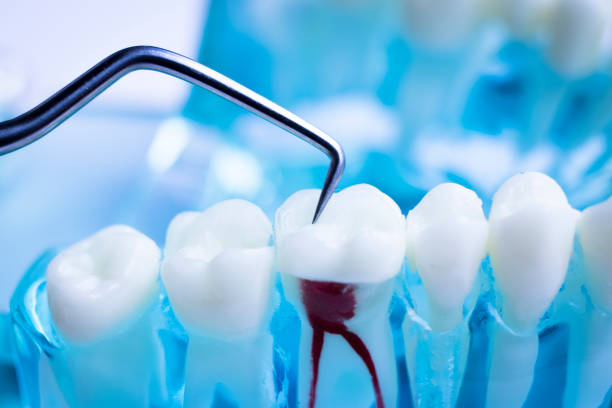
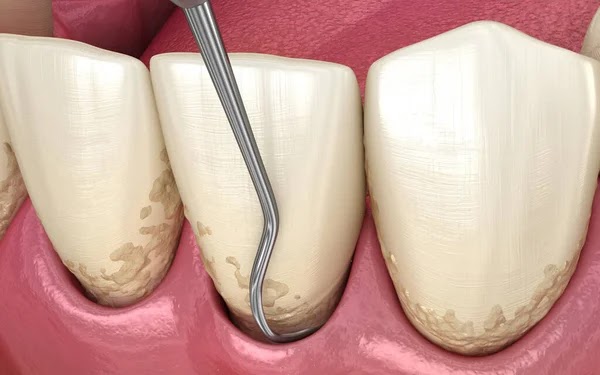
Scaling and root planing
A deep cleaning procedure performed to remove plaque, calculus, and bacteria from the surfaces of teeth and roots, commonly done to treat gum disease.
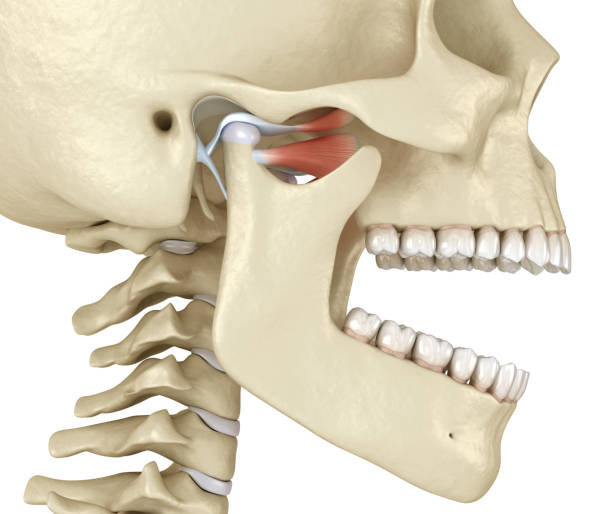
Temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ)
A condition charcterized by pain, dysfunction, or discomfort in the jaw joint and muscles controlling jaw movement.
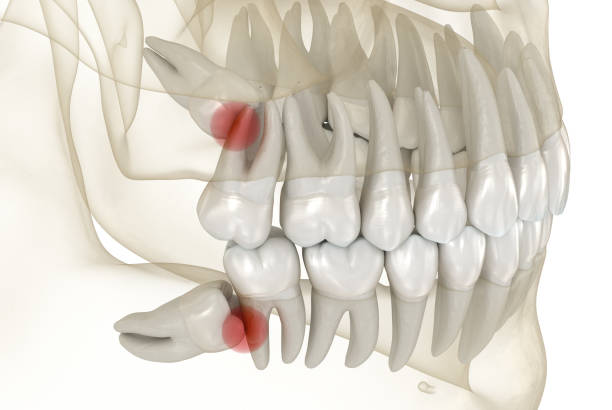
Wisdom Teeth
The third and final set of molars that people usually get in their late teens, early twenties. Wisdom teeth extraction is the surgical removal of the teeth if they currently cause problems or your dentist suspects them to cause problems in the future. Consult your dentist if you have any concerns.
Xerostomia (Dry mouth)
It is a condition characterized by reduced saliva production which can lead to discomfort and increased risk of dental problems.

Familiarizing yourself with dental terminology is a valuable step in becoming an informed and active participant in your oral health journey, so we hope this has been a helpful resource for you. Our goal is to help you achieve a brighter, healthier smile for years to come.Contact Dental Implants – Dr, Oscar Dalmao DPC today if you have any dental concerns, and we will be happy to schedule an appointment for you to speak with one of our oral health care providers.



